“I have a dream.”
The words are iconic. I’m sure most of us know the speaker, and the context.
Martin Luther King, Jr. The Lincoln Memorial in Washington, D.C. August 28, 1963.
Ground zero of the African-American civil rights movement.
 It had been 100 years since Abraham Lincoln himself had issued the Emancipation Proclamation. Almost 98 years since the U.S. Congress had passed the 13th amendment to the U.S. Constitution, abolishing slavery. A full century, in other words, to bring about full equality under the law for African Americans. But it hadn’t happened.
It had been 100 years since Abraham Lincoln himself had issued the Emancipation Proclamation. Almost 98 years since the U.S. Congress had passed the 13th amendment to the U.S. Constitution, abolishing slavery. A full century, in other words, to bring about full equality under the law for African Americans. But it hadn’t happened.
Three, four generations. And it still hadn’t happened. Bits and pieces, here and there, including a decade of rocky attempts at desegregating schools. But the 100-year old promise of freedom was far from fully realized.
And so African Americans were getting restless. Meetings were held, boycotts were enacted. People marched, people protested. Some began to think all this was not enough. A stronger voice was needed, a more powerful statement. Maybe even violence.
Into this world Martin Luther King came. Supporting Rosa Parks in her refusal to give her seat to a white passenger on an Alabama bus. Instrumental in organizing the civil rights movement. Preaching, speaking, rallying, lobbying. Insisting that, in their struggle for justice, African Americans must not resort to the same tactics as their oppressors: no hatred, no cruelty, no violence.
And this was how Martin Luther King, Jr., ended up on the steps of the Lincoln Memorial in Washington, D.C., on August 28, 1963, in front of 200,000 people.
Ground zero of the African-American civil rights movement.
“I have a dream.”
Powerful words, these. Powerful things, dreams.
“I have a dream that one day this nation will rise up and live out the true meaning of its creed: ‘We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal.’”
“I have a dream that my four little children will one day live in a nation where they will not be judged by the color of their skin but by the content of their character.”
“I have a dream that one day every valley shall be exalted, and every hill and mountain shall be made low, the rough places will be made plain, and the crooked places will be made straight; ‘and the glory of the Lord shall be revealed and all flesh shall see it together.’”
Sounds biblical, these words. Sounds like God, these dreams.
And that’s because they are.
Nearly two thousand years earlier another prophet had stood on the other side of the world in very similar circumstances. He, too, had a dream.
His name was Jesus. He was from Nazareth, in Galilee. His people, the Jews, were coming up to 100 years under Roman occupation: nearly a century of economic exploitation, heavy taxation, no freedom to choose their own course. Galilee in particular was a simmering cauldron of unrest, always ready to boil over into outright revolt.
It had happened before. Not long after Jesus was born, after the death of King Herod, several people tried to claim the throne to take a run at Rome. Messiahs grew like wildflowers after a spring rain—but they were ruthlessly cut down.
Ten years later—about the time Luke’s Jesus was turning heads as a child in Jerusalem’s Temple—a man named Judah led an outright revolt against Rome, claiming Rome’s heavy taxes amounted to slavery. He and his followers were brutally crushed by the armies of Rome.
And now here Jesus stands, on those very hills of Galilee.
Ground zero of the Jewish resistance movement.
“I have a dream,” Jesus declares.
“I have a dream of God’s kingdom come, God’s will being done, on earth as it is in heaven. On that day every valley shall be exalted, and every hill and mountain shall be made low, the rough places will be made plain, and the crooked places will be made straight; ‘and the glory of the Lord shall be revealed and all flesh shall see it together.’”
 “I have a dream,” Jesus proclaims to his fellow Galileans buckling under the weight of Rome. “I have a dream that one day those who are now grieving will be comforted, those who are now lowly and downtrodden will be in charge, those who are right now starving for justice will have their craving satisfied. I have a dream that one day those who are humble in their spirit and pure in their motives, those who show mercy toward others, those who make peace instead of inflicting violence and waging war, these will live in the fullness of life.”
“I have a dream,” Jesus proclaims to his fellow Galileans buckling under the weight of Rome. “I have a dream that one day those who are now grieving will be comforted, those who are now lowly and downtrodden will be in charge, those who are right now starving for justice will have their craving satisfied. I have a dream that one day those who are humble in their spirit and pure in their motives, those who show mercy toward others, those who make peace instead of inflicting violence and waging war, these will live in the fullness of life.”
“I have a dream today!” The crowd rumbles its agreement.
“I have a dream,” Jesus shouts to the restless masses. “I have a dream that one day the last will be first and the first will be last, everyone on equal footing. The Jew will live alongside the Gentile, the rich will sit down with the poor, men and women and elders and children all will share their lives in mutual care and respect.”
“I have a dream today!” You can hear the “Amen!” shouted in the background.
“I have a dream that one day the lost will be found. The struggling, the sick, the stigmatized, the silent, the sinner, all will be brought in to the banquet of God’s great love, the very least feasting until they are satisfied. I have a dream that one day the poor will hear good news for a change, the unwell will know true healing, the outcasts will be embraced, and those left for dead will experience new life.”
“I have a dream that one day oppression will cease and wars will be no more. The powerful and proud will be humbled and the lowly will be lifted up, swords will be turned into plows and seeds of life will be planted for the flourishing of humanity.”
“I have a dream today!” And the applause echoes out over the waters of the Sea of Galilee.
It might seem strange to think about Jesus’ teaching on the kingdom of God as God’s dream for the world. But that’s essentially the idea: the kingdom of God is God’s vision for the world, what the world would be like if people lived out God’s will, God’s way for humanity. The kingdom of God is the best possible world God can imagine.
This still might seem odd, to imagine God dreaming, to think of God imagining a better world. But remember: God is the Creator of all things, and to speak of God as Creator is to speak of God as imagining. Before anything existed, God imagined it. Everything that is, exists because God imagined it first. To use the Apostle Paul’s words, God is the one who “calls into being the things that do not yet exist.”
But God is not done imagining. God is not done dreaming. God has a dream for a better world. And God’s dream for the world is what Jesus called “the kingdom of God.”
And here’s the thing about God’s dreams: when God dreams something, you know it will become reality, even if it takes an eternity.
In fact, God has provided a way for us to see this dream become a reality: through Jesus. Jesus didn’t just stand on the steps of the halls of power and share God’s dream. He taught how this kingdom of God can come down to earth, and then he lived it out. Think back to the story of Jesus.
![Title: The parable of the sower [Click for larger image view]](https://i0.wp.com/diglib.library.vanderbilt.edu/cdri/jpeg/Mafa039.jpg) God’s kingdom, Jesus says, starts small, like a mustard seed. God’s dream for the world begins in the insignificant spaces in our lives: the everyday, the ordinary, the mundane. God’s dream for the world starts in the hidden places of our lives: in small, unseen acts of empathy and humility and compassion.
God’s kingdom, Jesus says, starts small, like a mustard seed. God’s dream for the world begins in the insignificant spaces in our lives: the everyday, the ordinary, the mundane. God’s dream for the world starts in the hidden places of our lives: in small, unseen acts of empathy and humility and compassion.
The kingdom of God does not come about through flashy programs and glitzy marketing campaigns, but through the nitty-gritty, down-to-earth, day-by-day, moment-by-moment choices we make to be kind, to be patient, to welcome, to forgive, to trust, to rejoice, to persevere.
God’s kingdom, Jesus says, spreads quietly, like yeast in dough. As we do these ordinary acts of love in the hidden spaces of the world, God’s dream begins to spread. It’s contagious. Grace begets grace. Forgiving others leads to others forgiving. Practising empathy and compassion encourages others to do the same. Joyful hospitality and thankful generosity multiply, spawning a community of open-handed and open-hearted people.
The kingdom of God does not come about through guilt manipulation or aggressive coercion, but through the repeated, repeated, repeated practice of Christ-likeness: humbling ourselves, raising up others, seeking the good of all above our own whiny wants.
And this is where God’s dream gets really hard. Because living into God’s kingdom, Jesus says, requires us to lose our lives in order to truly live. If we really want to seek first God’s kingdom and God’s justice, to see God’s dream become reality, Jesus says we must “deny ourselves and take up our cross and follow him.”
The kingdom of God does not come about by an easy road, a life of comfort and ease, insisting on our rights and privileges. It comes about by a narrow path, the path of willingly putting others’ genuine needs before our own personal preferences, seeking the good of all rather than our own selfish whims, knowing that when we all thrive together, we will each thrive even more.
And this is where God’s dream moves beyond our private lives and into the public domain. Because living into God’s kingdom, Jesus says, requires us to stand fast against evil: both that within ourselves and that in the wider world. God’s dream confronts the nightmare of this world’s evil. It demands that we defy those impulses within ourselves that cause harm to the other, and also those larger patterns of hostility and injustice within our societies that cause harm to whole swaths of people.
Racism, sexism, and bigotry of all kinds. Physical, sexual, and other forms of abuse. Economic exploitation and political repression. All the human rulers and underlying ideologies and prevailing attitudes and social structures that support these and other terrible evils.
To seek first God’s dream for the world means we are committing ourselves to stand firm against all these spiritual forces of evil—but to do so through persuasion and not coercion, through compassion and not cruelty, through mercy and not vengeance, through peaceful means and not violence.
Jesus walked this path himself, this narrow path to God’s kingdom. He did the small things, off in a back corner of the Roman Empire. He lived out the infectious way of welcoming love and selfless compassion and grateful joy. He resisted the evil powers of his day, willing to die rather than kill, giving his own life to seek the good of all.
And through all this Jesus sowed the seed of God’s kingdom in the world. In Jesus this dream was plucked from the fertile imagination of God and planted in the earthy soil of our humanity.
This was why, when Jesus was asked when God’s kingdom would come, when God’s dream would become a reality, Jesus could say: “Don’t look for the big, flashy signs! The kingdom of God is already among you. It’s right here—if you’re ready to see it.”
Do you remember the story of Pentecost? After Jesus’ death and resurrection, after Jesus’ exaltation to his rightful place in the universe, the wind of God moved on the face of the deep, just like it did in the beginning. God’s Spirit came upon that ragtag band of Jesus-followers, all huddled together in hope and fear.
And when it came time for the Apostle Peter to explain what was going on to the bewildered crowds, do you remember what Peter said? He quoted the words of the prophet Joel:
I will pour out my Spirit upon all flesh,
and your sons and your daughters shall prophesy,
and your young ones shall see visions,
and your old ones shall dream dreams.
And so it has been ever since.
God’s daughters and sons are still prophesying, they are still dreaming. The young ones, even the old ones—did you hear that?—are still dreaming God’s dreams for the world.
For two thousand years God’s people have been dreaming the dreams of God, imagining God’s kingdom come, God’s will being done, on earth as it is in heaven. Martin Luther King’s dream is just one of those dreams, still awaiting its full realization. Like the dreams of Syrian refugees, and residential school survivors, and many, many others.
The kingdom of God starts small, like a mustard seed. And it can take an age until its branches provide nests for the birds and shade for all who seek it. The arc of the moral universe is long, but it bends surely toward justice.
But to see this become a reality we must dream the dreams of God. We must imagine the world as it can be, flowing with justice and peace and bursting with flourishing life. Only then can we step out in faith and love and hope in the footsteps of Jesus, and grasp the dream that stands before us.
————————————-
Adapted from a sermon preached on October 30, 2016, at Morden Mennonite Church, as part of the “Stirring Our Imagination” worship series. Watch MLK’s full “I have a dream” speech; or listen to the audio recording. Images: 1) U.S. National Archives and Records Administration; 2) “Jesus Teaches By the Sea” by James Tissot; 3) “Parable of the Sower” by Jesus Mafa.
© Michael W. Pahl
 In Jesus I see a God who dreams of a better world, a kingdom of justice and peace and flourishing life, and who dares to plant that dream in the world with such a small and insignificant seed: love.
In Jesus I see a God who dreams of a better world, a kingdom of justice and peace and flourishing life, and who dares to plant that dream in the world with such a small and insignificant seed: love.









 God. God is depicted in a myriad of different ways in Scripture. These are all metaphors: God is in some sense comparable to a “Father,” for instance, or a “Mother,” or a “Lord,” or a “Rock,” just to name a few. Even “God” is a metaphor: God is analogous to the “gods” of other nations and religions, comparable to what we typically think of when we think of a “deity.” Some biblical descriptions, however, take a different tack: God is YHWH, “I Am Who I Am,” for instance, or God is “the one in whom we live and move and have our being,” or “God is love.” When I speak of “God,” I’m thinking more along those lines: God is “the ground and source of all being, personhood, and love.” I don’t imagine that God is merely “a being,” a distinct being within the universe, like us only bigger and stronger and immortal and invisible.
God. God is depicted in a myriad of different ways in Scripture. These are all metaphors: God is in some sense comparable to a “Father,” for instance, or a “Mother,” or a “Lord,” or a “Rock,” just to name a few. Even “God” is a metaphor: God is analogous to the “gods” of other nations and religions, comparable to what we typically think of when we think of a “deity.” Some biblical descriptions, however, take a different tack: God is YHWH, “I Am Who I Am,” for instance, or God is “the one in whom we live and move and have our being,” or “God is love.” When I speak of “God,” I’m thinking more along those lines: God is “the ground and source of all being, personhood, and love.” I don’t imagine that God is merely “a being,” a distinct being within the universe, like us only bigger and stronger and immortal and invisible. heaven. The Bible doesn’t speak of “heaven” as “our eternal home.” The New Testament understanding of life after death is simply being “with the Lord” or “with Christ.” In the end this includes living in transformed bodies in a renewed earthly creation (“resurrection” to a “new heavens and new earth”). In the Bible “heaven” means either 1) “the skies,” 2) “God’s dwelling,” or 3) a roundabout way of saying “God” (e.g. “kingdom of heaven” = “kingdom of God”). I don’t use the word “heaven” very often myself because of how it is misunderstood, but when I do it’s along the lines of 2) above: “the ‘place’ where God is most ‘fully present.’” Usually I use the word to speak of the biblical hope of “heaven” come down to earth, God’s presence being fully realized among us within a renewed creation.
heaven. The Bible doesn’t speak of “heaven” as “our eternal home.” The New Testament understanding of life after death is simply being “with the Lord” or “with Christ.” In the end this includes living in transformed bodies in a renewed earthly creation (“resurrection” to a “new heavens and new earth”). In the Bible “heaven” means either 1) “the skies,” 2) “God’s dwelling,” or 3) a roundabout way of saying “God” (e.g. “kingdom of heaven” = “kingdom of God”). I don’t use the word “heaven” very often myself because of how it is misunderstood, but when I do it’s along the lines of 2) above: “the ‘place’ where God is most ‘fully present.’” Usually I use the word to speak of the biblical hope of “heaven” come down to earth, God’s presence being fully realized among us within a renewed creation. sin. We tend to think of “sin” as “personal moral failure”: we’ve crossed a boundary established by God, and these boundaries are mostly related to our private lives or individual relationships. This way of thinking about sin isn’t wrong, it’s just incomplete, and if this is the only way we think about sin then it can be unhelpful and unhealthy. I think a better (and more holistically biblical) way of thinking about sin is as “all the ways we harm others, ourselves, and the natural world through our settled thoughts, our words, our actions, and our inaction.” This “harm” can be thought of as “preventing or hindering flourishing life.” With regard to people this can most practically be understood as keeping them from having their most basic needs met: needs for clean air and water, nutritious food, basic health, security and freedom, meaningful relationships, love and respect. This sin is more than just “personal moral failure,” then—it also includes collective sins such as systemic injustice, as well as actions that harm the natural world.
sin. We tend to think of “sin” as “personal moral failure”: we’ve crossed a boundary established by God, and these boundaries are mostly related to our private lives or individual relationships. This way of thinking about sin isn’t wrong, it’s just incomplete, and if this is the only way we think about sin then it can be unhelpful and unhealthy. I think a better (and more holistically biblical) way of thinking about sin is as “all the ways we harm others, ourselves, and the natural world through our settled thoughts, our words, our actions, and our inaction.” This “harm” can be thought of as “preventing or hindering flourishing life.” With regard to people this can most practically be understood as keeping them from having their most basic needs met: needs for clean air and water, nutritious food, basic health, security and freedom, meaningful relationships, love and respect. This sin is more than just “personal moral failure,” then—it also includes collective sins such as systemic injustice, as well as actions that harm the natural world. salvation. In Scripture the language of “salvation” is most often about “rescue” or “deliverance” from some real-life peril, but it also can include ideas of “healing” and “restoration,” whether physically or relationally, individually or collectively. Then there’s all the related biblical words like “redemption,” “reconciliation,” and so on, which are really variations on the “restoration” idea. When I speak of “salvation” or being “saved” or God as “Saviour,” I mean something along the lines of “God delivering us from all the ways we harm others, ourselves, and the natural world, and bringing about a full and flourishing life for all creation.” I don’t mean “God rescuing us from future eternal torture so that we can live a disembodied existence somewhere else forever with God.”
salvation. In Scripture the language of “salvation” is most often about “rescue” or “deliverance” from some real-life peril, but it also can include ideas of “healing” and “restoration,” whether physically or relationally, individually or collectively. Then there’s all the related biblical words like “redemption,” “reconciliation,” and so on, which are really variations on the “restoration” idea. When I speak of “salvation” or being “saved” or God as “Saviour,” I mean something along the lines of “God delivering us from all the ways we harm others, ourselves, and the natural world, and bringing about a full and flourishing life for all creation.” I don’t mean “God rescuing us from future eternal torture so that we can live a disembodied existence somewhere else forever with God.” kingdom of God. In much popular thinking the “kingdom of God” or “kingdom of heaven” is equivalent to “heaven,” which is thought of as “our eternal home” (see “heaven” above). But for early Jews, including Jesus and the authors of the New Testament, “kingdom of God” was a way of referring to “God ruling over God’s people and all the peoples of the earth.” When I use the phrase “kingdom of God,” I’m trying to capture Jesus’ particular understanding of this earthly rule of God, something along the lines of “God’s vision of a world of justice, peace, and flourishing life, which becomes a reality when people live according to God’s way of love.”
kingdom of God. In much popular thinking the “kingdom of God” or “kingdom of heaven” is equivalent to “heaven,” which is thought of as “our eternal home” (see “heaven” above). But for early Jews, including Jesus and the authors of the New Testament, “kingdom of God” was a way of referring to “God ruling over God’s people and all the peoples of the earth.” When I use the phrase “kingdom of God,” I’m trying to capture Jesus’ particular understanding of this earthly rule of God, something along the lines of “God’s vision of a world of justice, peace, and flourishing life, which becomes a reality when people live according to God’s way of love.”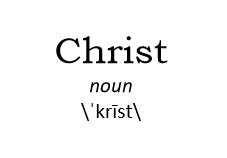 Jesus Christ. “Christ” is not Jesus’ second name; “Christ” is a title. And it’s not a title of divinity; it’s a human title. “Christ,” or “Messiah,” was most commonly a way of referring to the human kings in the line of ancient Israel’s King David. Eventually it came to refer to the ultimate Messiah, “the king from David’s dynasty who brings about God’s kingdom on earth.” The phrase “Jesus Christ,” then is a mini-creed: “Jesus is the one who makes real God’s vision of justice, peace, and life on earth.”
Jesus Christ. “Christ” is not Jesus’ second name; “Christ” is a title. And it’s not a title of divinity; it’s a human title. “Christ,” or “Messiah,” was most commonly a way of referring to the human kings in the line of ancient Israel’s King David. Eventually it came to refer to the ultimate Messiah, “the king from David’s dynasty who brings about God’s kingdom on earth.” The phrase “Jesus Christ,” then is a mini-creed: “Jesus is the one who makes real God’s vision of justice, peace, and life on earth.” Son of God. This phrase has a dual meaning in the New Testament. Some writings, Mark’s Gospel, for example, use “Son of God” in one of its Old Testament senses, as a way of referring to the kings in the line of David. In this sense the phrase is equivalent to “Christ” or “Messiah,” and has no overtones of divinity. Other writings, most notably John’s Gospel, use “Son of God” with a clear implication of divinity. I believe both to be true of Jesus, and how I use this phrase tends to depend on which New Testament books I’m talking about: Jesus is “the one who makes real God’s vision of justice, peace, and life on earth,” and Jesus is “the one who uniquely embodies God, showing us most clearly and completely who God is and how God works in the world.”
Son of God. This phrase has a dual meaning in the New Testament. Some writings, Mark’s Gospel, for example, use “Son of God” in one of its Old Testament senses, as a way of referring to the kings in the line of David. In this sense the phrase is equivalent to “Christ” or “Messiah,” and has no overtones of divinity. Other writings, most notably John’s Gospel, use “Son of God” with a clear implication of divinity. I believe both to be true of Jesus, and how I use this phrase tends to depend on which New Testament books I’m talking about: Jesus is “the one who makes real God’s vision of justice, peace, and life on earth,” and Jesus is “the one who uniquely embodies God, showing us most clearly and completely who God is and how God works in the world.” Jesus is Lord. This doesn’t mean “Jesus controls everything that happens.” Nor does it merely mean “Jesus is the boss of me.” “Lord” in the ancient world had connotations of “master,” yes, but it was also a common way of speaking of human rulers—kings, emperors, and the like. With none of these was the idea that they controlled a person’s life circumstances; it was that they commanded their obedience or allegiance. To say that “Jesus is Lord,” then, means that “Jesus is greater than all human rulers and any powers-that-be in this world, and so he holds our ultimate allegiance in all things.”
Jesus is Lord. This doesn’t mean “Jesus controls everything that happens.” Nor does it merely mean “Jesus is the boss of me.” “Lord” in the ancient world had connotations of “master,” yes, but it was also a common way of speaking of human rulers—kings, emperors, and the like. With none of these was the idea that they controlled a person’s life circumstances; it was that they commanded their obedience or allegiance. To say that “Jesus is Lord,” then, means that “Jesus is greater than all human rulers and any powers-that-be in this world, and so he holds our ultimate allegiance in all things.”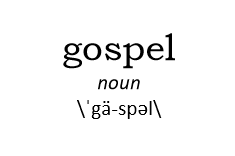 gospel. The New Testament word “gospel” means “good news.” The “gospel” is not merely that “God sent Jesus to die for our sins so that we can be forgiven and go to heaven when we die.” It’s the “good news that God has acted in Jesus—through his life, teachings, death, and resurrection—to make right everything that has gone wrong in the world.” In other words, it’s a way of summing up pretty much everything I’ve described above.
gospel. The New Testament word “gospel” means “good news.” The “gospel” is not merely that “God sent Jesus to die for our sins so that we can be forgiven and go to heaven when we die.” It’s the “good news that God has acted in Jesus—through his life, teachings, death, and resurrection—to make right everything that has gone wrong in the world.” In other words, it’s a way of summing up pretty much everything I’ve described above. faith. We tend to think of “faith” either as “believing certain things to be true,” or “trusting in someone to do something.” The New Testament language of “faith” includes those ideas, but also others: “faith” (pistis) can mean everything from “belief” to “trust” to “faithfulness” to “fidelity” to “allegiance.” When I use the word “faith” I can mean any or all of those, following the New Testament usage. All of those are the response God desires from us: “believing what God says to be true, trusting in God through all things, being faithful to God and following God’s way of love.”
faith. We tend to think of “faith” either as “believing certain things to be true,” or “trusting in someone to do something.” The New Testament language of “faith” includes those ideas, but also others: “faith” (pistis) can mean everything from “belief” to “trust” to “faithfulness” to “fidelity” to “allegiance.” When I use the word “faith” I can mean any or all of those, following the New Testament usage. All of those are the response God desires from us: “believing what God says to be true, trusting in God through all things, being faithful to God and following God’s way of love.” love. Some people hear “love” and think “affection,” a surge of warmth and fondness toward others. Others hear “love” and think “tolerance,” acknowledging and accepting others and their actions with a kind of benign smilingness. Some, perhaps conditioned by Christianity, hear “love” and think “self-sacrifice.” Others, of course, hear “love” and think “romance” or even “sex”: physical, emotional, even erotic intimacy. None of these are bad, but on their own they are incomplete. In the New Testament, love is consistently portrayed as loving the way Jesus loved. It is more along the lines, then, of “freely giving ourselves for others so that they might experience flourishing life together with us, even if we feel they don’t deserve it, even when it hurts us to do so.” This love, I’m convinced, is at the heart of who God is, what Jesus taught and lived out unto death, and how God’s “salvation,” the “kingdom of God,” comes about.
love. Some people hear “love” and think “affection,” a surge of warmth and fondness toward others. Others hear “love” and think “tolerance,” acknowledging and accepting others and their actions with a kind of benign smilingness. Some, perhaps conditioned by Christianity, hear “love” and think “self-sacrifice.” Others, of course, hear “love” and think “romance” or even “sex”: physical, emotional, even erotic intimacy. None of these are bad, but on their own they are incomplete. In the New Testament, love is consistently portrayed as loving the way Jesus loved. It is more along the lines, then, of “freely giving ourselves for others so that they might experience flourishing life together with us, even if we feel they don’t deserve it, even when it hurts us to do so.” This love, I’m convinced, is at the heart of who God is, what Jesus taught and lived out unto death, and how God’s “salvation,” the “kingdom of God,” comes about.




![Title: The parable of the sower [Click for larger image view]](https://i0.wp.com/diglib.library.vanderbilt.edu/cdri/jpeg/Mafa039.jpg)