John’s Gospel opens with one of the most beautiful and spectacular theological reflections in all of Scripture. Here are the well-known first few verses:
In the beginning was the Word, and the Word was with God, and the Word was God. He was in the beginning with God. All things came into being through him, and without him not one thing came into being. What has come into being in him was life, and the life was the light of all people. The light shines in the darkness, and the darkness did not overtake it. (1:1-5)
Later we’re told that this Word “became flesh and lived among us” (1:14)—the Word, then, is a description of Jesus, whose story this prologue is introducing.
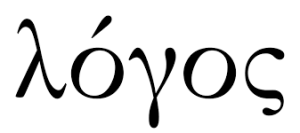 But what does it mean to describe Jesus as “the Word” (λόγος)? Here’s but a partial glance at this profound description of Jesus. This summary is more technical than most of what I put on my blog—if it’s all Greek to you, just skip it and pretend you never saw it.
But what does it mean to describe Jesus as “the Word” (λόγος)? Here’s but a partial glance at this profound description of Jesus. This summary is more technical than most of what I put on my blog—if it’s all Greek to you, just skip it and pretend you never saw it.
First, let’s talk about Old Testament background. Divine word language in the Hebrew Bible has two main specific referents: 1) the Torah or its specific commands as “word(s) (of God/the Lord)”; and 2) individual prophetic oracles as “word (of God/the Lord).” There are also some more general references to a variety of ways in which God speaks “word(s),” most significantly God’s creative/life-giving “word.”
All of these carry with them the idea of “word” (דָּבָר) as a “spoken message”; in some way, God is conceived as speaking out these messages, and they have effect. This relates very strongly, by the way, to the Hebrew conception of obedience as “hearing (the voice)”: if we well and truly hear God’s spoken message, we will obey. Which holds true, incidentally, even with God’s creative/life-giving “word”; God speaks light and life and the creation obeys. This connection of דָּבָר with orality is likely still present even in other uses of דָּבָר, such as when it simply means a “thing” or a “matter.”
Second, let’s talk about New Testament context. While the OT ideas carry on to some degree, divine word language in the NT—“word (of God/the Lord),” or even “word of (some divine characteristic like ‘grace’ or ‘truth’)”—has one predominant referent: the gospel about Jesus proclaimed orally by the apostles. Again, this carries with it the idea of “word” (usually λόγος but also ῥῆμα, following the interchangeability of these in the Old Greek/LXX translation of דָּבָר,) as a spoken message. And, as with the OT, there’s an element of orality present in pretty much all of the uses of λόγος (and even ῥῆμα) in the NT.
This dominant Scriptural background and context makes it most likely that John 1 uses “word” (λόγος) in the same way: as a divine “spoken message.” This is supported by the echoes of uses of divine word language in the Hebrew Bible, especially allusions to Genesis 1 in John 1:1-4 (cf. God’s creative/life-giving “word” above) and the explicit contrast/comparison with the Torah in John 1:17 (cf, God’s command(s) as “word(s)” above).
This is further supported by the use of λόγος throughout John’s Gospel. If λόγος in John 1 refers to Hellenistic philosophical concepts, such as the Stoic λόγος as the fundamental principle of the cosmos or the Neo-Platonic λόγος as the force which gives matter shape and life, it is very odd that the rest of the Gospel makes no further allusions to these—or at least no clear and indisputable allusions. Instead, it uses divine word language in all the ways noted above, following Hebrew Bible and other early Christian usage.
But isn’t there some resonance with Proverbs’ wisdom hymn (8:22-31)? I think that’s likely. But a direct correspondence with the λόγος in John 1 has a problem: if John’s primary referent for λόγος is Proverbs’ Wisdom, why doesn’t he use σοφία instead? That’s the Old Greek/LXX’s translation of Proverbs’ חָכְמָה, after all. “In the beginning was Wisdom” would make that connection explicit.
The typical solution to this problem is to say that John gets at Proverbs’ wisdom through Hellenistic philosophy: Proverbs’ wisdom got connected in Hellenistic Judaism to Stoicism’s or Neo-Platonism’s λόγος, and John gets his λόγος from Stoicism or Neo-Platonism, with Proverbs’ wisdom thrown in. However, this has problems, especially the one noted above, that no further echoes of a Greek philosophical λόγος can be easily detected in the rest of the Gospel (not to mention the fact that Neo-Platonism, if that’s the perceived background, didn’t emerge for another two centuries).
A related solution to this problem is to invoke Philo of Alexandria, a Jew around Jesus’ time who did try to bring together Judaism and Greek philosophy. Philo makes the connection between the “spirit of God” in Genesis 1:2 and a kind of Platonic understanding of the λόγος. However, this still doesn’t get at the connection with Proverbs’ wisdom. Also, it has the same problem as the general Hellenistic influence theory above: the lack of usage of λόγος in these ways through the rest of John’s Gospel.
A much better way of getting around this problem is a simpler and more direct one: John himself (or someone else in early Judaism/Christianity) did some similar creative work to Philo but in a different direction, making the connection between Proverbs’ wisdom and the Hebrew Bible’s divine word, probably through the link of creation. Proverbs 8 refers to wisdom’s role in creation; λόγος can refer to God’s creative/life-giving word; therefore these can be linked. No Stoicism or Philo required.
By the way, I don’t hold to some notion of a “pure first-century Judaism” that was not Hellenized; all early Judaism was Hellenized to a greater or lesser degree. But that’s the thing: the Hellenization of early Judaism was a bit of a messy spectrum, with various kinds and degrees of influence of Greek culture and thought on early Jewish culture and thought. And I just don’t see a high degree of Hellenistic influence in John’s Gospel (contra Bultmann, who saw it in every nook and cranny).
What’s the upshot of all this? The divine word in John 1, the λόγος, is God’s spoken message, God’s creative and life-giving message, God’s commanding message, God’s prophetic message, God’s good-news message, spoken in the past through the prophets but now spoken pre-eminently through a Son—even made flesh in this beloved Son, Jesus of Nazareth.
© Michael W. Pahl








 Or, to sharpen the question even further: How can we reconcile the Jesus of Revelation 19 with the Jesus of the Gospels? What happened to “
Or, to sharpen the question even further: How can we reconcile the Jesus of Revelation 19 with the Jesus of the Gospels? What happened to “ This word of God is a powerful word—but it cuts two ways. The message of good news for the oppressed means judgment on the oppressors. The word of comfort for the brokenhearted is a denunciation of all who break those hearts. The promise of freedom for all held captive is a blunt warning to their captors.
This word of God is a powerful word—but it cuts two ways. The message of good news for the oppressed means judgment on the oppressors. The word of comfort for the brokenhearted is a denunciation of all who break those hearts. The promise of freedom for all held captive is a blunt warning to their captors.