Have you ever had two people understand something you’ve said in two very different ways? It happens to all of us sometime. I’ve had it happen to me when I preach, more than once. This happens even when I use common Christian words or phrases derived from the Bible—maybe especially when I do so. It can be a little disconcerting, to say the least.
Part of this is just me needing to look for ways to communicate more clearly. Part of it, however, is our natural tendency to hear what we expect to hear. When we’re in a church and someone speaks about “faith” or “heaven,” for example, or they say “Jesus saves us from our sins,” we are inclined to hear those things in a particular “churchy” or “Christianese” kind of way.
But many of these words or phrases don’t mean for me what they often mean in popular Christianity. The reason? I don’t think the popular understandings actually reflect the biblical ideas behind these words or phrases, at least not completely.
Well, if you’re ever in doubt about what I might mean when I talk about “salvation,” or when I say, “Jesus is Lord,” I’ve created this nifty little guide: Michael Pahl’s Handy-Dandy Handbook of Christian Words and Phrases. Who knows? Maybe I’ll start handing this out before I preach every Sunday.
 God. God is depicted in a myriad of different ways in Scripture. These are all metaphors: God is in some sense comparable to a “Father,” for instance, or a “Mother,” or a “Lord,” or a “Rock,” just to name a few. Even “God” is a metaphor: God is analogous to the “gods” of other nations and religions, comparable to what we typically think of when we think of a “deity.” Some biblical descriptions, however, take a different tack: God is YHWH, “I Am Who I Am,” for instance, or God is “the one in whom we live and move and have our being,” or “God is love.” When I speak of “God,” I’m thinking more along those lines: God is “the ground and source of all being, personhood, and love.” I don’t imagine that God is merely “a being,” a distinct being within the universe, like us only bigger and stronger and immortal and invisible.
God. God is depicted in a myriad of different ways in Scripture. These are all metaphors: God is in some sense comparable to a “Father,” for instance, or a “Mother,” or a “Lord,” or a “Rock,” just to name a few. Even “God” is a metaphor: God is analogous to the “gods” of other nations and religions, comparable to what we typically think of when we think of a “deity.” Some biblical descriptions, however, take a different tack: God is YHWH, “I Am Who I Am,” for instance, or God is “the one in whom we live and move and have our being,” or “God is love.” When I speak of “God,” I’m thinking more along those lines: God is “the ground and source of all being, personhood, and love.” I don’t imagine that God is merely “a being,” a distinct being within the universe, like us only bigger and stronger and immortal and invisible.
 heaven. The Bible doesn’t speak of “heaven” as “our eternal home.” The New Testament understanding of life after death is simply being “with the Lord” or “with Christ.” In the end this includes living in transformed bodies in a renewed earthly creation (“resurrection” to a “new heavens and new earth”). In the Bible “heaven” means either 1) “the skies,” 2) “God’s dwelling,” or 3) a roundabout way of saying “God” (e.g. “kingdom of heaven” = “kingdom of God”). I don’t use the word “heaven” very often myself because of how it is misunderstood, but when I do it’s along the lines of 2) above: “the ‘place’ where God is most ‘fully present.’” Usually I use the word to speak of the biblical hope of “heaven” come down to earth, God’s presence being fully realized among us within a renewed creation.
heaven. The Bible doesn’t speak of “heaven” as “our eternal home.” The New Testament understanding of life after death is simply being “with the Lord” or “with Christ.” In the end this includes living in transformed bodies in a renewed earthly creation (“resurrection” to a “new heavens and new earth”). In the Bible “heaven” means either 1) “the skies,” 2) “God’s dwelling,” or 3) a roundabout way of saying “God” (e.g. “kingdom of heaven” = “kingdom of God”). I don’t use the word “heaven” very often myself because of how it is misunderstood, but when I do it’s along the lines of 2) above: “the ‘place’ where God is most ‘fully present.’” Usually I use the word to speak of the biblical hope of “heaven” come down to earth, God’s presence being fully realized among us within a renewed creation.
 sin. We tend to think of “sin” as “personal moral failure”: we’ve crossed a boundary established by God, and these boundaries are mostly related to our private lives or individual relationships. This way of thinking about sin isn’t wrong, it’s just incomplete, and if this is the only way we think about sin then it can be unhelpful and unhealthy. I think a better (and more holistically biblical) way of thinking about sin is as “all the ways we harm others, ourselves, and the natural world through our settled thoughts, our words, our actions, and our inaction.” This “harm” can be thought of as “preventing or hindering flourishing life.” With regard to people this can most practically be understood as keeping them from having their most basic needs met: needs for clean air and water, nutritious food, basic health, security and freedom, meaningful relationships, love and respect. This sin is more than just “personal moral failure,” then—it also includes collective sins such as systemic injustice, as well as actions that harm the natural world.
sin. We tend to think of “sin” as “personal moral failure”: we’ve crossed a boundary established by God, and these boundaries are mostly related to our private lives or individual relationships. This way of thinking about sin isn’t wrong, it’s just incomplete, and if this is the only way we think about sin then it can be unhelpful and unhealthy. I think a better (and more holistically biblical) way of thinking about sin is as “all the ways we harm others, ourselves, and the natural world through our settled thoughts, our words, our actions, and our inaction.” This “harm” can be thought of as “preventing or hindering flourishing life.” With regard to people this can most practically be understood as keeping them from having their most basic needs met: needs for clean air and water, nutritious food, basic health, security and freedom, meaningful relationships, love and respect. This sin is more than just “personal moral failure,” then—it also includes collective sins such as systemic injustice, as well as actions that harm the natural world.
 salvation. In Scripture the language of “salvation” is most often about “rescue” or “deliverance” from some real-life peril, but it also can include ideas of “healing” and “restoration,” whether physically or relationally, individually or collectively. Then there’s all the related biblical words like “redemption,” “reconciliation,” and so on, which are really variations on the “restoration” idea. When I speak of “salvation” or being “saved” or God as “Saviour,” I mean something along the lines of “God delivering us from all the ways we harm others, ourselves, and the natural world, and bringing about a full and flourishing life for all creation.” I don’t mean “God rescuing us from future eternal torture so that we can live a disembodied existence somewhere else forever with God.”
salvation. In Scripture the language of “salvation” is most often about “rescue” or “deliverance” from some real-life peril, but it also can include ideas of “healing” and “restoration,” whether physically or relationally, individually or collectively. Then there’s all the related biblical words like “redemption,” “reconciliation,” and so on, which are really variations on the “restoration” idea. When I speak of “salvation” or being “saved” or God as “Saviour,” I mean something along the lines of “God delivering us from all the ways we harm others, ourselves, and the natural world, and bringing about a full and flourishing life for all creation.” I don’t mean “God rescuing us from future eternal torture so that we can live a disembodied existence somewhere else forever with God.”
 kingdom of God. In much popular thinking the “kingdom of God” or “kingdom of heaven” is equivalent to “heaven,” which is thought of as “our eternal home” (see “heaven” above). But for early Jews, including Jesus and the authors of the New Testament, “kingdom of God” was a way of referring to “God ruling over God’s people and all the peoples of the earth.” When I use the phrase “kingdom of God,” I’m trying to capture Jesus’ particular understanding of this earthly rule of God, something along the lines of “God’s vision of a world of justice, peace, and flourishing life, which becomes a reality when people live according to God’s way of love.”
kingdom of God. In much popular thinking the “kingdom of God” or “kingdom of heaven” is equivalent to “heaven,” which is thought of as “our eternal home” (see “heaven” above). But for early Jews, including Jesus and the authors of the New Testament, “kingdom of God” was a way of referring to “God ruling over God’s people and all the peoples of the earth.” When I use the phrase “kingdom of God,” I’m trying to capture Jesus’ particular understanding of this earthly rule of God, something along the lines of “God’s vision of a world of justice, peace, and flourishing life, which becomes a reality when people live according to God’s way of love.”
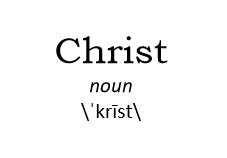 Jesus Christ. “Christ” is not Jesus’ second name; “Christ” is a title. And it’s not a title of divinity; it’s a human title. “Christ,” or “Messiah,” was most commonly a way of referring to the human kings in the line of ancient Israel’s King David. Eventually it came to refer to the ultimate Messiah, “the king from David’s dynasty who brings about God’s kingdom on earth.” The phrase “Jesus Christ,” then is a mini-creed: “Jesus is the one who makes real God’s vision of justice, peace, and life on earth.”
Jesus Christ. “Christ” is not Jesus’ second name; “Christ” is a title. And it’s not a title of divinity; it’s a human title. “Christ,” or “Messiah,” was most commonly a way of referring to the human kings in the line of ancient Israel’s King David. Eventually it came to refer to the ultimate Messiah, “the king from David’s dynasty who brings about God’s kingdom on earth.” The phrase “Jesus Christ,” then is a mini-creed: “Jesus is the one who makes real God’s vision of justice, peace, and life on earth.”
 Son of God. This phrase has a dual meaning in the New Testament. Some writings, Mark’s Gospel, for example, use “Son of God” in one of its Old Testament senses, as a way of referring to the kings in the line of David. In this sense the phrase is equivalent to “Christ” or “Messiah,” and has no overtones of divinity. Other writings, most notably John’s Gospel, use “Son of God” with a clear implication of divinity. I believe both to be true of Jesus, and how I use this phrase tends to depend on which New Testament books I’m talking about: Jesus is “the one who makes real God’s vision of justice, peace, and life on earth,” and Jesus is “the one who uniquely embodies God, showing us most clearly and completely who God is and how God works in the world.”
Son of God. This phrase has a dual meaning in the New Testament. Some writings, Mark’s Gospel, for example, use “Son of God” in one of its Old Testament senses, as a way of referring to the kings in the line of David. In this sense the phrase is equivalent to “Christ” or “Messiah,” and has no overtones of divinity. Other writings, most notably John’s Gospel, use “Son of God” with a clear implication of divinity. I believe both to be true of Jesus, and how I use this phrase tends to depend on which New Testament books I’m talking about: Jesus is “the one who makes real God’s vision of justice, peace, and life on earth,” and Jesus is “the one who uniquely embodies God, showing us most clearly and completely who God is and how God works in the world.”
 Jesus is Lord. This doesn’t mean “Jesus controls everything that happens.” Nor does it merely mean “Jesus is the boss of me.” “Lord” in the ancient world had connotations of “master,” yes, but it was also a common way of speaking of human rulers—kings, emperors, and the like. With none of these was the idea that they controlled a person’s life circumstances; it was that they commanded their obedience or allegiance. To say that “Jesus is Lord,” then, means that “Jesus is greater than all human rulers and any powers-that-be in this world, and so he holds our ultimate allegiance in all things.”
Jesus is Lord. This doesn’t mean “Jesus controls everything that happens.” Nor does it merely mean “Jesus is the boss of me.” “Lord” in the ancient world had connotations of “master,” yes, but it was also a common way of speaking of human rulers—kings, emperors, and the like. With none of these was the idea that they controlled a person’s life circumstances; it was that they commanded their obedience or allegiance. To say that “Jesus is Lord,” then, means that “Jesus is greater than all human rulers and any powers-that-be in this world, and so he holds our ultimate allegiance in all things.”
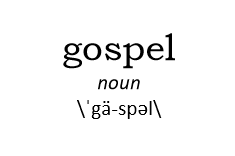 gospel. The New Testament word “gospel” means “good news.” The “gospel” is not merely that “God sent Jesus to die for our sins so that we can be forgiven and go to heaven when we die.” It’s the “good news that God has acted in Jesus—through his life, teachings, death, and resurrection—to make right everything that has gone wrong in the world.” In other words, it’s a way of summing up pretty much everything I’ve described above.
gospel. The New Testament word “gospel” means “good news.” The “gospel” is not merely that “God sent Jesus to die for our sins so that we can be forgiven and go to heaven when we die.” It’s the “good news that God has acted in Jesus—through his life, teachings, death, and resurrection—to make right everything that has gone wrong in the world.” In other words, it’s a way of summing up pretty much everything I’ve described above.
 faith. We tend to think of “faith” either as “believing certain things to be true,” or “trusting in someone to do something.” The New Testament language of “faith” includes those ideas, but also others: “faith” (pistis) can mean everything from “belief” to “trust” to “faithfulness” to “fidelity” to “allegiance.” When I use the word “faith” I can mean any or all of those, following the New Testament usage. All of those are the response God desires from us: “believing what God says to be true, trusting in God through all things, being faithful to God and following God’s way of love.”
faith. We tend to think of “faith” either as “believing certain things to be true,” or “trusting in someone to do something.” The New Testament language of “faith” includes those ideas, but also others: “faith” (pistis) can mean everything from “belief” to “trust” to “faithfulness” to “fidelity” to “allegiance.” When I use the word “faith” I can mean any or all of those, following the New Testament usage. All of those are the response God desires from us: “believing what God says to be true, trusting in God through all things, being faithful to God and following God’s way of love.”
 love. Some people hear “love” and think “affection,” a surge of warmth and fondness toward others. Others hear “love” and think “tolerance,” acknowledging and accepting others and their actions with a kind of benign smilingness. Some, perhaps conditioned by Christianity, hear “love” and think “self-sacrifice.” Others, of course, hear “love” and think “romance” or even “sex”: physical, emotional, even erotic intimacy. None of these are bad, but on their own they are incomplete. In the New Testament, love is consistently portrayed as loving the way Jesus loved. It is more along the lines, then, of “freely giving ourselves for others so that they might experience flourishing life together with us, even if we feel they don’t deserve it, even when it hurts us to do so.” This love, I’m convinced, is at the heart of who God is, what Jesus taught and lived out unto death, and how God’s “salvation,” the “kingdom of God,” comes about.
love. Some people hear “love” and think “affection,” a surge of warmth and fondness toward others. Others hear “love” and think “tolerance,” acknowledging and accepting others and their actions with a kind of benign smilingness. Some, perhaps conditioned by Christianity, hear “love” and think “self-sacrifice.” Others, of course, hear “love” and think “romance” or even “sex”: physical, emotional, even erotic intimacy. None of these are bad, but on their own they are incomplete. In the New Testament, love is consistently portrayed as loving the way Jesus loved. It is more along the lines, then, of “freely giving ourselves for others so that they might experience flourishing life together with us, even if we feel they don’t deserve it, even when it hurts us to do so.” This love, I’m convinced, is at the heart of who God is, what Jesus taught and lived out unto death, and how God’s “salvation,” the “kingdom of God,” comes about.
How do you understand these words? What often-misunderstood “Christian words” would you add?
© Michael W. Pahl





 If that sounds like liturgy, that’s because it is. This was the commitment I made before our congregation when I was installed as pastor. Really, then, my 2017 pastoral New Year’s goal is simply re-committing myself to this calling.
If that sounds like liturgy, that’s because it is. This was the commitment I made before our congregation when I was installed as pastor. Really, then, my 2017 pastoral New Year’s goal is simply re-committing myself to this calling. Be bold in proclaiming the gospel of Jesus Christ. This is something I have been doing—every sermon I preach is a proclamation of the gospel—but I am resolved (yes, on this I’m “resolved”) to do this even more. Our world—and each one of us—desperately needs to hear God’s good news again and again and again. But beware: this is not the gospel many of us grew up with. It’s the
Be bold in proclaiming the gospel of Jesus Christ. This is something I have been doing—every sermon I preach is a proclamation of the gospel—but I am resolved (yes, on this I’m “resolved”) to do this even more. Our world—and each one of us—desperately needs to hear God’s good news again and again and again. But beware: this is not the gospel many of us grew up with. It’s the  Nobody said U.S. politics were dull.
Nobody said U.S. politics were dull. To borrow another favourite metaphor of Jesus—and some direct teaching from the Apostle Paul—“we reap what we sow” (
To borrow another favourite metaphor of Jesus—and some direct teaching from the Apostle Paul—“we reap what we sow” (





